Toxic megacolon
 Print-Friendly
Print-Friendly
Toxic dilation of the colon; Megarectum; Inflammatory bowel disease - toxic megacolon; Crohn disease - toxic megacolon; Ulcerative colitis - toxic megacolon
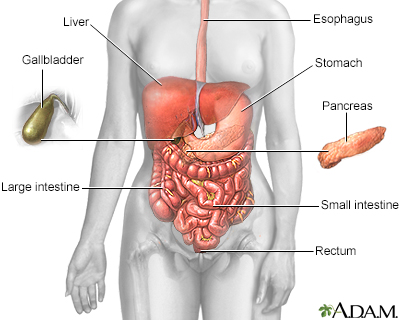
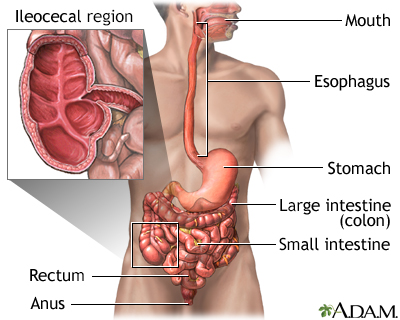
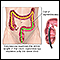
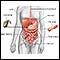
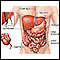
Toxic megacolon occurs when swelling and inflammation spread into the deeper layers of your colon. As a result, the colon stops working and widens. In severe cases, the colon may rupture.
I Would Like to Learn About:
Causes
The term "toxic" means that this problem is very dangerous. Toxic megacolon may occur in people with an inflamed colon due to:
- Ulcerative colitis, or Crohn disease that is not well controlled
- Infections of the colon such as Clostridioides difficile
- Ischemic bowel disease (ischemic colitis)
Other forms of megacolon include pseudo-obstruction, acute colonic ileus, or congenital colonic dilation. These conditions do not involve an infected or inflamed colon.
Symptoms
The rapid widening of the colon may cause the following symptoms to occur over a short period of time:
- Painful, distended abdomen
- Fever (sepsis)
- Diarrhea (usually bloody)
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam. Findings may include:
- Tenderness in the abdomen
- Reduced or absent bowel sounds
The exam may reveal signs of septic shock, such as:
- Increased heart rate
- Mental status changes
- Rapid heart rate
- Low blood pressure
The provider may order any of the following tests:
- Abdominal x-ray, ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI scan
- Blood electrolytes
- Complete blood count
Treatment
Treatment of the disorder that led to toxic megacolon includes:
- Steroids and other medicines that suppress the immune system
- Antibiotics
If you have septic shock, you will be admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) of the hospital. Treatment may include:
- Breathing machine (mechanical ventilation)
- Dialysis for kidney failure
- Fluids given directly into a vein
- Medicines to treat low blood pressure, infection, or prior blood clotting
- Oxygen
If rapid colon widening is not treated, an opening or rupture can form in it. If the condition doesn't improve with medical treatment, surgery will be needed to remove part or all of the colon.
You may receive antibiotics to prevent sepsis (a severe infection).
Outlook (Prognosis)
If the condition does not improve, it can be fatal. Colon surgery is usually needed in such cases.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Perforation of the colon
- Sepsis
- Shock
- Death
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Go to the emergency room or call the local emergency number (such as 911) if you develop severe abdominal pain, especially if you also have:
- Bloody diarrhea
- Fever
- Frequent diarrhea
- Rapid heart rate
- Tenderness when the abdomen is pressed
- Abdominal distention
Prevention
Treating diseases that cause toxic megacolon, such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn disease, can prevent this condition.
Related Information
| Ulcerative colitis...Crohn disease | Ulcerative colitis...Crohn disease - In... |
References
Efron JE. Large bowel: Management of toxic megacolon. In: Cameron J, ed. Current Surgical Therapy. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:177-286.
Lichtenstein GR. Inflammatory bowel disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 127.
Thomas N, Wu AW. Large intestine. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 81.