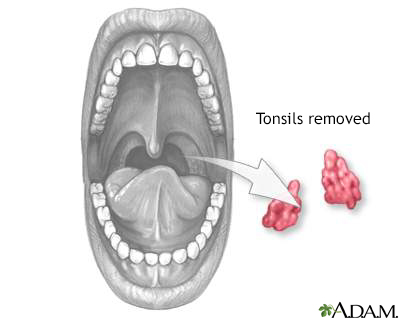
Tonsillectomies and children
 Print-Friendly
Print-Friendly
Children and tonsillectomies
Today, many parents wonder if it is wise for children to have their tonsils taken out. Tonsillectomy may be recommended if your child has any of the following:
- Difficulty swallowing
- Obstructed breathing during sleep
- Throat infections or throat abscesses that keep returning
In most cases, inflammation of the tonsils can be successfully treated with antibiotics. There are always risks associated with surgery.
You and your child's health care provider may consider a tonsillectomy if:
- Your child has frequent infections (7 or more times in 1 year, 5 or more times per year over 2 years, or 3 or more times per year over 3 years).
- Your child misses a lot of school.
- Your child snores, has trouble breathing, and has sleep apnea.
- Your child has an abscess or growth on their tonsils.
I Would Like to Learn About:
Information
Today, many parents wonder if it is wise for children to have their tonsils taken out. Tonsillectomy may be recommended if your child has any of the following:
- Difficulty swallowing
- Obstructed breathing during sleep
- Throat infections or throat abscesses that keep returning
In most cases, inflammation of the tonsils can be successfully treated with antibiotics. There are always risks associated with surgery.
You and your child's health care provider may consider a tonsillectomy if:
- Your child has frequent infections (7 or more times in 1 year, 5 or more times per year over 2 years, or 3 or more times per year over 3 years).
- Your child misses a lot of school.
- Your child snores, has trouble breathing, and has sleep apnea.
- Your child has an abscess or growth on their tonsils.
Related Information
References
Goldstein NA. Evaluation and management of pediatric obstructive sleep apnea. In: Lesperance MM, ed. Cummings Pediatric Otolaryngology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 3.
Mitchell RB, Archer SM, Ishman SL, et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: tonsillectomy in children (update). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019;160(1_suppl):S1-S42. PMID: 30798778 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30798778/.
Wetmore RF. Tonsils and adenoids. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 411.