Muscle strain treatment
 Print-Friendly
Print-Friendly
Treatment - muscle strain
Question:
How do you treat a muscle strain?
Answer:
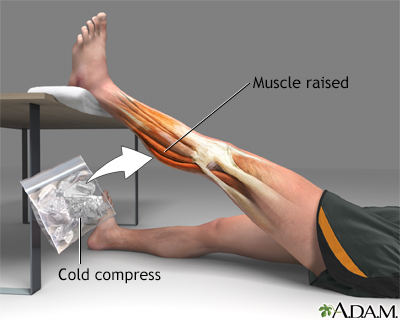
Rest the strained muscle and apply ice for the first few days after the injury. Anti-inflammatory medicines such as ibuprofen, naproxen, or acetaminophen (Tylenol) also help reduce pain and swelling. As the pain decreases, you can use heat on the muscle. Stretching and light exercises to bring blood to the injured area can also be useful. In general, stretching and warm compresses are helpful before exercises. Cooling down and icing the area after exercise can help.
Get medical help right away if:
- You have a lot of swelling with the muscle strain.
- You can't move your arms, legs, or joints.
- You have swelling that is getting worse as time passes.
I Would Like to Learn About:
Information
Question:
How do you treat a muscle strain?
Answer:
Rest the strained muscle and apply ice for the first few days after the injury. Anti-inflammatory medicines such as ibuprofen, naproxen, or acetaminophen (Tylenol) also help reduce pain and swelling. As the pain decreases, you can use heat on the muscle. Stretching and light exercises to bring blood to the injured area can also be useful. In general, stretching and warm compresses are helpful before exercises. Cooling down and icing the area after exercise can help.
Get medical help right away if:
- You have a lot of swelling with the muscle strain.
- You can't move your arms, legs, or joints.
- You have swelling that is getting worse as time passes.
Related Information
References
Biundo JJ. Bursitis, tendinitis, and other periarticular disorders and sports medicine. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 247.
Geiderman JM, Torbati S. General principles of orthopedic injuries. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 41.
Wang D, Eliasberg CD, Rodeo SA. Physiology and pathophysiology of musculoskeletal tissues. In: Miller MD, Thompson SR. eds. DeLee, Drez, & Miller's Orthopaedic Sports Medicine. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 1.