
Urinary 24 hours sodium; Urine Na+
The sodium urine test measures the amount of sodium in the urine.
Sodium can also be measured in a blood sample.
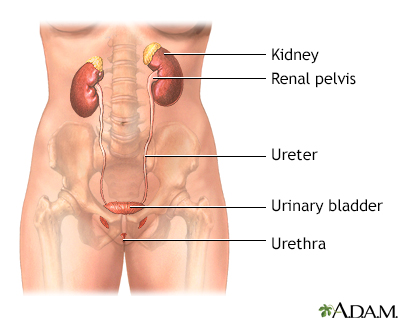
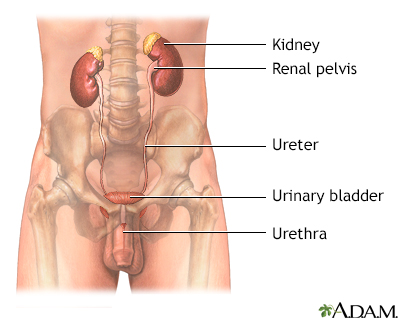
After you provide a urine sample, it is tested in the lab. If needed, your health care provider may ask you to collect your urine at home over 24 hours. Your provider will tell you how to do this. Follow instructions exactly so that the results are accurate.
Your provider will ask you to temporarily stop taking any medicines that may affect the test result. Tell your provider about all the medicines you take, including:
DO NOT stop taking any medicine before talking to your provider.
The test involves only normal urination. There is no discomfort.
The test is often used to help determine the cause of an abnormal sodium blood level. It also checks whether your kidneys are removing sodium from the body. It may be used to diagnose or monitor many types of kidney diseases.
For adults, normal urine sodium values are generally more than 20 mEq/L in a random urine sample and 40 to 220 mEq (40 to 220 mmol) per day. Your result depends on how much fluid and sodium or salt you take in.
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test result.
A higher than normal urine sodium level may be due to:
A lower than normal urine sodium level may be a sign of:
There are no risks with this test.
Al-Awqati Q, Radhakrishnan J. Disorders of sodium and water. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 102.
Gharavi AG, Landry DW. Approach to the patient with renal disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 100.
Kamel KS, Halperin ML. Interpretation of electrolyte and acid-base parameters in blood and urine. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 24.
Oh MS, Briefel G, Pincus MR. Evaluation of renal function, water, electrolytes, and acid-base balance. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 15.
Verbalis JG. Disorders of water balance. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 15.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 7/13/2025
Reviewed By: Laura J. Martin, MD, MPH, ABIM Board Certified in Internal Medicine and Hospice and Palliative Medicine, Atlanta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, also known as the American Accreditation HealthCare Commission (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics and subscribes to the principles of the Health on the Net Foundation (www.hon.ch). |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.